Category













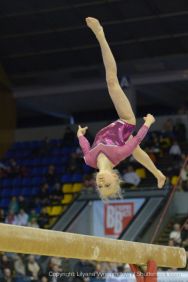
























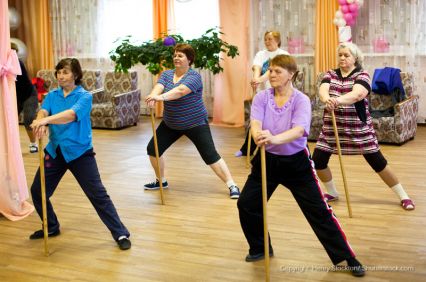




















The defining characteristic of the Command Style is to exactly reproduce and replicate an anticipated response or performance in a short period of time so that the specific Command Style objectives in subject matter and behavior can be developed. Cognitively, the Command Style emphasizes automaticity-an immediate synchronized, orchestrated performance.
Category













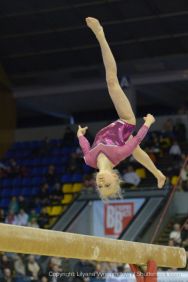
























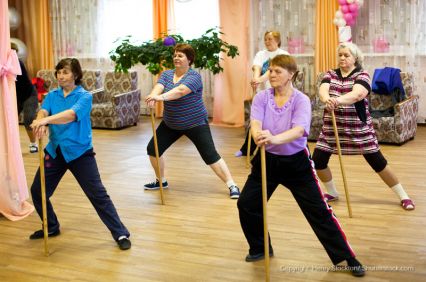




















In the Command Style, the teacher makes the maximum number of decisions in all three sets of the Anatomy while the learner initiates the minimum number of decisions, which is the decision to participate or not to participate. The teacher’s role (T) is to make all decisions in each set of the anatomy. The learner’s role (L) is to reproduce, follow, replicate on cue the teacher’s decisions to achieve a precision performance that follows the cues and pace and rhythm decisions that has been established for replicating the content.

When the Command Style behavior is achieved, the following objectives in subject matter are emphasized*:
When the Command Style behavior is achieved, the following objectives in behavior are emphasized*:
*Not all subject matter and behavior objectives are the focal point in every teaching episode. The task determines which objectives are the primary focus of the learning experience and which are supporting objectives.